Investment grade life insurance is the best passive investment vehicle available for Canadians to use inside corporations and holding companies. The main reason? It’s tax-exempt.
But first, let’s back up and look at other passive investments. The growth on passive investments in Canadian Corporations and Holding Companies such as stocks, bonds, mutual funds, ETFs and real estate are taxed at 50% in Ontario.
By comparison, money inside life insurance grows tax-free whether it is owned personally or owned by Corporations and Holding Companies.
Tax efficiency is why life insurance generally performs better than most other asset classes. In order for a Canadian entrepreneur to outperform life insurance in a 50% tax environment, they would need to take large investment risks. Oftentimes, taking that amount of risk can result in negative returns in any particular year. It’s an easy way for an investor to lose his shirt.
Let’s look at the real facts and numbers. Here’s a quick breakdown, over the last 20 years, of the performance of the main asset classes familiar to Canadian investors: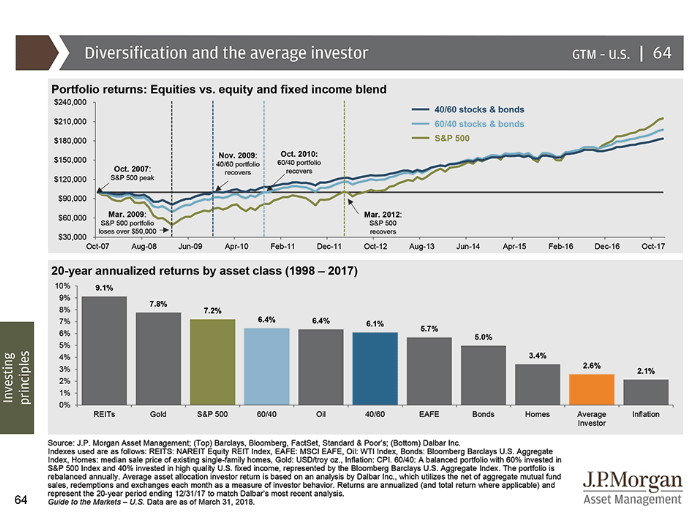
One particular thing highlighted in the chart is the annualized rate of return of average investors being at 2.6%. This is mainly attributed to “emotional investing”, meaning that most investors buy high (when the market is doing well) and sell low (when the market is in a correction).
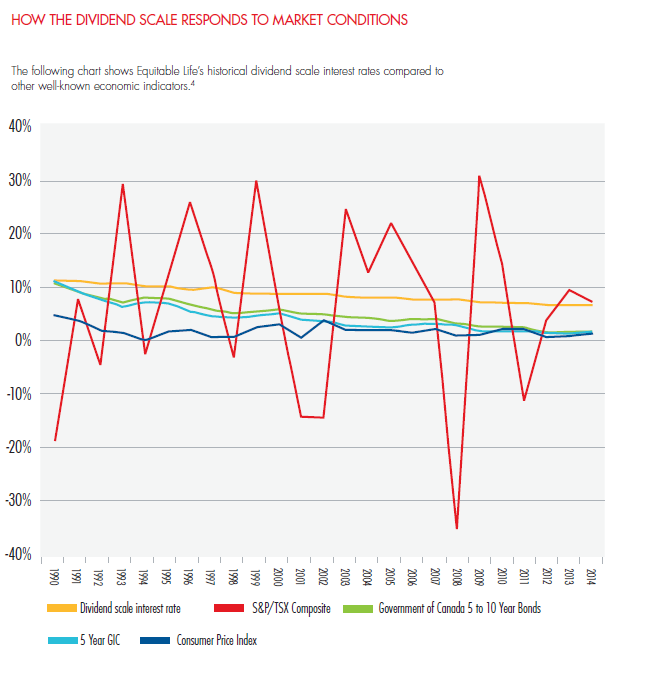
Now, for an idea of how whole life insurance generally compares, let’s take a look at Equitable Life’s whole life dividend scale (one of the best whole life contracts in Canada):
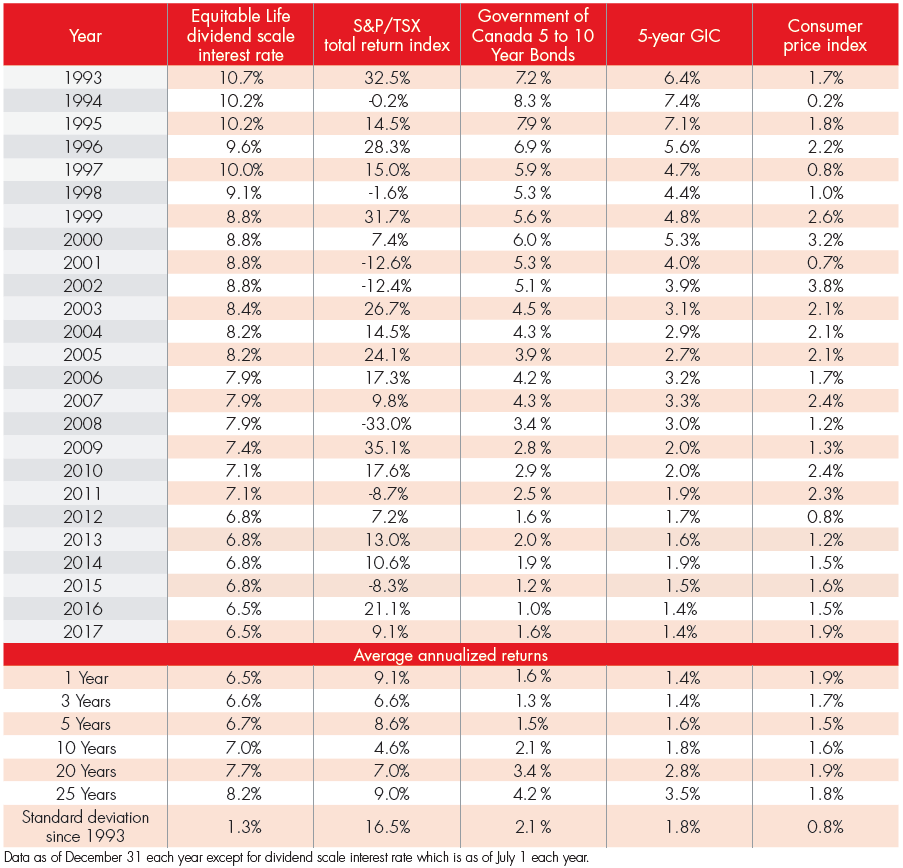
 The numbers don’t lie. Whole life insurance has outperformed most investment types in the last 20-25 years. As a matter of fact, whole life insurance has had an average rate of return of about 9% per year in the last 60 years.
The numbers don’t lie. Whole life insurance has outperformed most investment types in the last 20-25 years. As a matter of fact, whole life insurance has had an average rate of return of about 9% per year in the last 60 years.
But there’s more to it. Whole life insurance as an investment also prevents investors from making major emotional mistakes. When stock markets are collapsing, typical investors fear losing all their money and when markets are performing extremely well, investors have a fear of missing out on great rates of return.
This general behaviour leads investors to buy high and sell low. A big advantage with whole life insurance is that it offers consistent rates of return on an annual basis. Once the cash value and death benefit of your insurance is at a specific value, it will not go down. The cash value and death benefit will keep going up and up each year.
How Life Insurance Works Inside Corporations/Holding Companies
The major advantage that life insurance has over other assets is it tax-haven status. Life insurance in Canada is the only tax shelter available for passive investments inside corporations or holding companies that are normally taxed at 50%. If you add the 50% passive investments tax on other asset types, it is clear that whole life insurance is the best performing after-tax asset class in Canada in the last 20-25 years.
Additionally, whole life insurance is much less volatile than other asset classes. Canadian life insurance companies have offered whole life insurance for over 100 years and they have paid dividends each and every year. Whole life insurance has gone through two world wars, the great depression, the tech bubble crash in the early 2000s, and the financial market crash of 2008 without seeing a negative rate of return.
Many Canadians think that life insurance isn’t a great investment vehicle because they believe the cash invested inside of life insurance will be used by their beneficiaries rather than used as retirement income.
However, that is entirely false. The cash value inside life insurance can be utilized to supplement retirement income on a tax-preferred basis.
Now, I’m certainly not saying that you should invest all your holding company assets inside life insurance. However, I’ve seen incorporated business owners experience a lot of success in the past when including whole life insurance as an asset class in their portfolio.
If you’re interested in learning more about how you can help grow and protect your wealth tax-free, book a complimentary one-on-one online meeting with me today. As your Certified Financial Planner, I’ll gather quotes from independent life insurance companies to find the best value for your specific situation (it can often be a six-figure difference or more). Then, we’ll work together to put your wealth to work for you.

Accepting Applications starting April 6th – Canada Emergency Response Benefit (CERB)
/in 2020 Only, blog, Coronavirus /by Bryan WilsonThe sheer volume of applications for the Canada Emergency Response Benefit (CERB) will likely overwhelm the system. If you or someone you know need to apply for this benefit, we suggest you prepare TODAY before the applications begin:
Double check your myCRA account username and password
Direct Deposit is setup
3 – 5 days via Direct Deposit vs 10 days via cheque in the mail
You should double check your myCRA username and password by signing in at:
If you do not have direct deposit setup with CRA, you can set it up TODAY at:
To help manage the volume, the CRA has setup specific days for you to apply based on month of birth.
If you were born in the month of:
January | February | March: Mondays – Best day to apply is April 6th
April | May | June: Tuesdays – Best day to apply is April 7th
July | August | September: Wednesdays – Best day to apply is April 8th
October | November | December: Thursdays – Best day to apply is April 9th
Fridays, Saturdays and Sundays are open for any birth month
Eligibility
The benefit will be available to workers:
Residing in Canada, who are at least 15 years old;
Who have stopped working because of COVID-19 and have not voluntarily quit their job or are eligible for EI regular or sickness benefits;
Who had income of at least $5,000 in 2019 or in the 12 months prior to the date of their application; and
Who are or expect to be without employment or self-employment income for at least 14 consecutive days in the initial four-week period. For subsequent benefit periods, they expect to have no employment or self-employment income.
Tax Loss Selling
/in 2020 Only, blog, Coronavirus, Investment, Tax /by Bryan WilsonOver the last few weeks, the financial market has taken a downturn amidst fears over Coronavirus.
Understandably, you are concerned with your portfolio, it’s important to stay level-headed to avoid making financial missteps. However, staying level-headed doesn’t necessarily mean you sit there and do nothing. In fact, one consideration you can look is taking an active tax management approach.
Tax loss selling is a strategy to crystallize or realize any capital losses in your non-registered accounts so it can be used to offset any capital gains. There is no benefit to selling in your tax free savings account (TFSA) or registered retirement savings plan (RRSP).
You can apply capital losses back 3 years or carry them forward indefinitely, therefore we’ve outlined several situations that make sense for tax loss selling.
To better understand how tax-loss selling works, imagine a scenario in which someone invests $100,000, putting $50,000 in “Investment A” and $50,000 in “Investment B.”
At the end of one year, Investment A has risen by $10,000 and is now worth $60,000. Investment B has declined by $10,000 and is now worth $40,000.
Without tax-loss selling, the investor has a realized gain of $10,000 from Investment A, and has a potential tax bill of $1,500 (assuming he or she sells the shares and pays the 15% capital gains tax on the profit).
On the other hand, with tax-loss selling, selling Investment B to offset gains from Investment A. At the end of the year, instead of paying a $1,500 tax, the investor only has a potential tax bill of $0, for a potential tax savings of $1,500.
With the investor’s tax liability reduced by $1,500, that savings becomes money that can be invested back in the portfolio, used to maximize RRSP contributions, pay off debt, or spend as one pleases.
What Situations make sense for tax loss selling?
If you have an investment with a considerable capital gain, review through your current investments to see if there are any investments to sell at a loss.
Receiving a tax refund for a previous year. Keep in mind, you can apply capital losses back 3 years, therefore if you sold a property within the last 3 years for a considerable gain and paid the tax. This year, you could sell other investments at a loss and apply them back and get some tax paid back.
For tax deferral, with tax losses you can apply these losses back 3 years or carry them forward indefinitely, therefore you may want to trigger a loss today because if you are planning to sell that property in the next year or so, it may rebound and therefore you will lose the chance to offset the gains.
Lastly, you may have an investment in your portfolio that’s a dud. It might be time to move on and put your money into a different investment so that you can apply the loss in the future.
Tax Loss Selling is Complicated
There are specific conditions required by CRA that must be met in order for this strategy to work such as making sure your loss is not declared a “superficial loss” (these rules are very restrictive). A superficial loss is when you sell and trigger a capital loss, you cannot deduct the loss if you or an affiliate purchase an identical security within 30 days before or after your settlement date.
Another condition is that the sale of assets is prior to the year-end deadline (this varies by calendar year). You also need to make sure you have accurate information on the adjusted cost base (ACB) of your investment. When you file your taxes, any losses must be first used to offset capital gains in the current tax year, then any remaining losses can be carried back.
Before engaging in tax loss selling, you should contact us directly so we can make the strategy works for you.
Do I Qualify for the Canada Emergency Response Benefit & EI?
/in 2020 Only, blog, Coronavirus /by Bryan WilsonTo help Canadians through this difficult time, the Federal Government created the Canada Emergency Response Benefit (CERB) and made changes to the Employment Insurance Program (EI). For those whose employment has affected by the Coronavirus, we have created a chart to help you figure out which program you qualify for and provide links to apply for each program.
The Federal Government has already made numerous changes to these programs so we will be updating this document whenever a change to the program is made.
Stay home and stay safe.
Help for Small/Medium Businesses & Entrepreneurs – 75% wage subsidy, $40,000 interest-free loan & more
/in 2020 Only, blog, Business Owners /by Bryan WilsonMarch 27, 2019 – Prime Minister Justin Trudeau announced programs and measures focused on helping Small & Medium Sized Businesses and Entrepreneurs cope with the economic consequences caused by the COVID-19 pandemic.
Wage Subsidy increased to 75%
The Prime Minister has been under pressure from the small business community to boost the wage subsidy beyond the 10% initially announced to help keep people employed. Today, Mr. Trudeau announced the government will increase the wage subsidy from 10% to 75% to help keep employees on the payroll. This increase will be backdated to Sunday, March 15th.
Canada Emergency Business Account (CEBA)
The CEBA will allow banks to offer $40,000 loans that will be interest-free for the 1st year which will be guaranteed by the government. If you meet certain conditions, $10,000 of the loan can be forgivable.
Defer GST, HST, Duty
The government will defer GST & HST payments, as well as duty and taxes owed on imports until June 2020.
Bank of Canada Rate Cut
Bank of Canada slashed its key overnight interest rate to 0.25%.
Full details and qualification requirements will be available on Monday.
Canada Emergency Response Benefit to help workers and businesses
/in 2020 Only, blog /by Bryan Wilson$2,000/month for 4 months – Canada Emergency Response Benefit to help workers and businesses
To support workers and help businesses keep their employees, the government has proposed legislation to establish the Canada Emergency Response Benefit (CERB). This taxable benefit would provide $2,000 a month for up to four months for workers who lose their income as a result of the COVID-19 pandemic. The CERB would be a simpler and more accessible combination of the previously announced Emergency Care Benefit and Emergency Support Benefit.
The CERB would cover Canadians who have lost their job, are sick, quarantined, or taking care of someone who is sick with COVID-19, as well as working parents who must stay home without pay to care for children who are sick or at home because of school and daycare closures. The CERB would apply to wage earners, as well as contract workers and self-employed individuals who would not otherwise be eligible for Employment Insurance (EI).
Additionally, workers who are still employed, but are not receiving income because of disruptions to their work situation due to COVID-19, would also qualify for the CERB. This would help businesses keep their employees as they navigate these difficult times, while ensuring they preserve the ability to quickly resume operations as soon as it becomes possible.
The EI system was not designed to process the unprecedented high volume of applications received in the past week. Given this situation, all Canadians who have ceased working due to COVID-19, whether they are EI-eligible or not, would be able to receive the CERB to ensure they have timely access to the income support they need.
Canadians who are already receiving EI regular and sickness benefits as of today would continue to receive their benefits and should not apply to the CERB. If their EI benefits end before October 3, 2020, they could apply for the CERB once their EI benefits cease, if they are unable to return to work due to COVID-19. Canadians who have already applied for EI and whose application has not yet been processed would not need to reapply. Canadians who are eligible for EI regular and sickness benefits would still be able to access their normal EI benefits, if still unemployed, after the 16-week period covered by the CERB.
The portal for accessing the CERB would be available in early April.
Canadians would begin to receive their CERB payments within 10 days of application. The CERB would be paid every four weeks and be available from March 15, 2020 until October 3, 2020.
How to apply for EI benefits for COVID-19 quarantines and other support programs
/in 2020 Only, blog /by Bryan WilsonWhat are EI benefits for those quarantined with COVID-19?
Employment Insurance (EI) sickness benefits provide up to 15 weeks of income replacement and is available to eligible claimants who are unable to work because of illness, injury or quarantine, to allow them time to restore their health and return to work. Canadians quarantined can apply for Employment Insurance (EI) sickness benefits.
Is there a waiting period?
For quarantine because of COVID-19, the one week waiting period is waived. Contact the new dedicated toll-free phone number if you are in quarantine and seeking to waive the one-week EI sickness benefits waiting period so you can be paid for the first week of your claim:
Telephone: 1-833-381-2725 (toll-free)
Teletypewriter (TTY): 1-800-529-3742
What benefits does EI offer?
Employment Insurance (EI) sickness benefits can provide you with up to 15 weeks of financial assistance if you cannot work for medical reasons. You could receive 55% of your earnings up to a maximum of $573 a week.
Who qualifies for EI sick-leave benefits?
Employed Canadians who pay EI premiums and self-employed people registered for access to EI may be eligible for sickness benefits.
There are a number of factors that determine eligibility. You need to demonstrate that:
you’re unable to work for medical reasons
your regular weekly earnings from work have decreased by more than 40% for at least one week
you accumulated 600 insured hours* of work in the 52 weeks before the start of your claim or since the start of your last claim, whichever is shorter
*As an example, 600 hours are equivalent to 20 weeks of work at 30 hours a week.
While you’re receiving sickness benefits, you must remain available for work if it weren’t for your medical condition.
If you are self-employed and pay into EI, you have to wait at least 12 months from the date of your confirmed registration before you are eligible for sickness benefits. You must also meet all of the following conditions:
The amount of time you spend on your business has decreased by more than 40% for at least one week because of your medical condition
You earned a minimum amount of self-employed earnings during the calendar year before the year you apply for benefits. To receive benefits for 2020, you need to have earned at least $7,279 in 2019
What if I don’t qualify for EI?
In April, the government will be introducing the Emergency Care Benefit providing up to $900 bi-weekly, for up to 15 weeks. This flat-payment Benefit would be administered through the Canada Revenue Agency (CRA) and provide income support to:
Workers, including the self-employed, who are quarantined or sick with COVID-19 but do not qualify for EI sickness benefits.
Workers, including the self-employed, who are taking care of a family member who is sick with COVID-19, such as an elderly parent, but do not qualify for EI sickness benefits.
Parents with children who require care or supervision due to school or daycare closures, and are unable to earn employment income, irrespective of whether they qualify for EI or not.
Application for the Benefit will be available in April 2020, and require Canadians to attest that they meet the eligibility requirements. They will need to re-attest every two weeks to reconfirm their eligibility. Canadians will select one of three channels to apply for the Benefit:
by accessing it on their CRA MyAccount secure portal;
by accessing it from their secure My Service Canada Account; or
by calling a toll free number equipped with an automated application process.
Do you need a Doctor’s note?
According to the Government of Canada’s website, people claiming EI sickness benefits due to quarantine will not have to provide a medical certificate.
How do I get started with the application for EI to see if I qualify?
The application for Employment Insurance can be found here:
Support for Business Owners and Employees Covid 19
/in 2020 Only, blog /by Bryan WilsonWe know that clients have questions about the Federal government’s economic response plan, we have included a summary of the information below for business owners, employees and other support that’s available. Please don’t hesitate to contact us. We’re here for you.
Government of Canada Covid-19 Economic Response Plan
For Business Owners
Wage Subsidy: To support businesses that are facing revenue losses and to help prevent lay-offs, the government is proposing to provide eligible small employers a temporary wage subsidy for a period of three months. The subsidy will be equal to 10% of remuneration paid during that period, up to a maximum subsidy of $1,375 per employee and $25,000 per employer. Businesses will be able to benefit immediately from this support by reducing their remittances of income tax withheld on their employees’ remuneration. Employers benefiting from this measure will include corporations eligible for the small business deduction, as well as non-profit organizations and charities. Eligible for those with payroll under $1M.
Work-Sharing Program to support your Employees
BDC Loan Expansion Facility– Details and contact information on tapping into the expanded credit. You must have been in business for at least two years; You must have more than $100,000 in annual gross revenues and should be profitable under normal operating conditions; Owners and/or business should have good credit history; The program enables business owners to apply for a Loan or Line of Credit with BDC for up to $100,000 to be repaid within five years. The interest rate is set today at 3.3%, which is very low for a business loan. The application is done on-line, and applicants would need to have various financial documents available to upload to complete the application. The processing time is about 2-3 weeks at present.
Purchase Order Financial available through BDC
Facebook announces $100M grant program for small businesses– Facebook announced yesterday that it’s creating a $100 million grant program for small businesses. Applications aren’t open yet, but the company says this will include both ad credits and cash grants that can be spent on operational costs like paying workers and paying rent. It will be available to up to 30,000 businesses in the 30-plus countries where Facebook operates. Facebook has also created a Business Hub with tips and resources for businesses trying to survive during the outbreak.
For Employees
Employment Insurance Information– Dedicated Covid-19 EI phone number 1-833-381-2725- The one-week waiting period for EI sickness benefits will be waived for new claimants who are quarantined so they can be paid for the first week of their claim
Tax support:
Extending the tax filing deadline to June 1
Allowing taxpayers to defer tax payments until after August 31 (for amounts that are due after today and before September)
Temporarily boosting of the Canada Child Benefit payments
Banks deferring mortgage payments for up to 6 months- RBC, TD, BMO, CIBC, Scotiabank & National Bank.
Emergency Care Benefit” which offers up to $900 biweekly (for up to 15 weeks) to provide income support to workers who have to stay home and don’t have access to paid sick leave.
Six-month, interest-free reprieve on student loan payments.
Life Insurance as an Investment for Canadian Corporations/Holding Companies: What They Are and How They Work
/in blog, Business Owners, corporate, Estate Planning, Insurance, Investment, Tax /by Bryan WilsonInvestment grade life insurance is the best passive investment vehicle available for Canadians to use inside corporations and holding companies. The main reason? It’s tax-exempt.
But first, let’s back up and look at other passive investments. The growth on passive investments in Canadian Corporations and Holding Companies such as stocks, bonds, mutual funds, ETFs and real estate are taxed at 50% in Ontario.
By comparison, money inside life insurance grows tax-free whether it is owned personally or owned by Corporations and Holding Companies.
Tax efficiency is why life insurance generally performs better than most other asset classes. In order for a Canadian entrepreneur to outperform life insurance in a 50% tax environment, they would need to take large investment risks. Oftentimes, taking that amount of risk can result in negative returns in any particular year. It’s an easy way for an investor to lose his shirt.
Let’s look at the real facts and numbers. Here’s a quick breakdown, over the last 20 years, of the performance of the main asset classes familiar to Canadian investors:
One particular thing highlighted in the chart is the annualized rate of return of average investors being at 2.6%. This is mainly attributed to “emotional investing”, meaning that most investors buy high (when the market is doing well) and sell low (when the market is in a correction).
Now, for an idea of how whole life insurance generally compares, let’s take a look at Equitable Life’s whole life dividend scale (one of the best whole life contracts in Canada):
But there’s more to it. Whole life insurance as an investment also prevents investors from making major emotional mistakes. When stock markets are collapsing, typical investors fear losing all their money and when markets are performing extremely well, investors have a fear of missing out on great rates of return.
This general behaviour leads investors to buy high and sell low. A big advantage with whole life insurance is that it offers consistent rates of return on an annual basis. Once the cash value and death benefit of your insurance is at a specific value, it will not go down. The cash value and death benefit will keep going up and up each year.
How Life Insurance Works Inside Corporations/Holding Companies
The major advantage that life insurance has over other assets is it tax-haven status. Life insurance in Canada is the only tax shelter available for passive investments inside corporations or holding companies that are normally taxed at 50%. If you add the 50% passive investments tax on other asset types, it is clear that whole life insurance is the best performing after-tax asset class in Canada in the last 20-25 years.
Additionally, whole life insurance is much less volatile than other asset classes. Canadian life insurance companies have offered whole life insurance for over 100 years and they have paid dividends each and every year. Whole life insurance has gone through two world wars, the great depression, the tech bubble crash in the early 2000s, and the financial market crash of 2008 without seeing a negative rate of return.
Many Canadians think that life insurance isn’t a great investment vehicle because they believe the cash invested inside of life insurance will be used by their beneficiaries rather than used as retirement income.
However, that is entirely false. The cash value inside life insurance can be utilized to supplement retirement income on a tax-preferred basis.
Now, I’m certainly not saying that you should invest all your holding company assets inside life insurance. However, I’ve seen incorporated business owners experience a lot of success in the past when including whole life insurance as an asset class in their portfolio.
If you’re interested in learning more about how you can help grow and protect your wealth tax-free, book a complimentary one-on-one online meeting with me today. As your Certified Financial Planner, I’ll gather quotes from independent life insurance companies to find the best value for your specific situation (it can often be a six-figure difference or more). Then, we’ll work together to put your wealth to work for you.
Click here to schedule a complimentary 1-on-1 online meeting with me today.
Financial Planning for Business Owners
/in blog, Business Owners, corporate /by Bryan WilsonFinancial Planning for business owners is often two-sided: personal financial planning and planning for the business.
Business owners have access to a lot of financial tools that employees don’t have access to; this is a great advantage, however it can be overwhelming too. A financial plan can relieve this.
A financial plan looks at where you are today and where you want to go. It determines your short, medium and long term financial goals and how you can reach them. For you, personally and for your business.
Why do you need a Financial Plan?
For a business owner, personal and business finances are connected. Therefore both sides should be addressed: Personal and Business.
What does a Financial Plan for a Business include?
There are 2 main sides your business financial plan should address: Growth and Preservation
Growth:
Preservation:
What does a Personal Financial Plan include?
There are 2 main sides your financial plan should address: Accumulation and Protection
Accumulation:
Protection:
What’s the Financial Planning Process?
Next steps…
Tax Series: Strategies for Private Corporations
/in blog, corporate, Tax /by Bryan WilsonLast summer, Finance Minister Morneau announced a number of tax reforms for Small Business Owners, including the changes to income sprinkling, minimizing the incentives to keep passive investments and reducing the transfer of corporate surpluses to capital gains.
This year’s Federal Budget focused on tax tightening measures for business owner:
● Small Business Tax Rate Reduction from 10% to 9%.
● Passive Investment Income held within the corp (Reduction begins at $50,000)
● Tax on Split Income
Since these changes will be effective January 1, 2019, a discussion and plan should be prioritized now, since 2018 will be the “prior year” of 2019. Life insurance is a great solution to help business owners address these problems.
Reduced Small Business Tax Rate
● Key Change: Effective January 1, 2019, the small business tax rate will be reduced from 10% to 9%
● Problem: Lower corporate tax rates result in more capital trapped inside the corporation.
● Possible Solution: Life Insurance Proceeds credit the capital dividend account on death allowing for tax-efficient distribution of funds from the corporation to the estate.
Limited Access to Small Business Tax Rate
● Key Change: Passive investment income greater than $50,000/year reduces the small business tax rate limit for small business tax rate. The business limit is reduced to zero at $150,000 of investment income.
● Problem: For companies with passive income over $50,000, the small business limit will be reduced and thus, increase the total amount of tax you have to pay.
● Possible Solution: Exempt life insurance does not produce passive investment income unless there is a disposition. Put a portion of corporations passive investments into a life insurance policy and reduce passive investment income and limit the erosion of the small business limit. Concepts such as Corporate Estate bond, Corporate Insured Retirement Program, Corporate held Critical Illness with Return of Premium
Tax on Split Income
● Key Change: Tax on split income (TOSI) rules extended to cover adult children in certain cases. Different rules depending on age of adult children
● Problem: For adult children receiving income and don’t pass the TOSI rules, income is taxed at the highest personal marginal tax rate on the first dollar. More trapped funds inside the corporation due to fewer tax-effective strategies.
● Possible Solution: Put a portion of corporation’s trapped surplus into a corporate owned life insurance policy which results in tax-efficient distribution of funds from the corporation to the estate.